FAQs
Those might have popped-up in your mind.
Categories
How to Create CSR with SAN Values Using OpenSSL ?
For creating CSR with SAN values (X.509 v3 Extension) it’s important to create a configuration file with the required certificate details. Execute following command in openssl.
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout pvtkey.cer -config config.cnf -out csr.txt -utf8It will create a Private key (pvtkey.cer) and CSR file (csr.txt).
Sample Configuration file (config.cnf)
[req]
prompt = no
distinguished_name = dn
req_extensions = ext
[dn]
CN = 192.168.2.23
O = Abc Corporation
L = Sydney
ST = New South Walse
C = AU
[ext]
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
IP.1 = 192.168.2.23
IP.2 = 10.12.4.112
DNS.1 = 192.168.2.23
DNS.2 = 10.12.4.112
DNS.3 = sms.abc.local
DNS.4 = localhostNote that you need to put City name against "L" (=Location), and 2 letter Country ISO code against "C" (=Country).
It will generate CSR with CN=192.168.2.23 and 3 SAN values: 10.12.4.112, sms.abc.local and localhost.
Notice that when IP address is there in CN or SAN, we need to put its value against both IP Address and DNS. For others (URL, Servername etc) only DNS value is required.
Tagged In
No Comments Yet.
How to create the CSR with SAN in Windows IIS ?
Following steps are applicable for all versions of IIS. Windows Server should be domain joined.
-
Open the MMC console and add the Certificate snap-in to it as Local Computer. Right Click Personal node on the left and Select All Tasks –>Advanced Operations –> Create Custom Request.
-
Choose Proceed without enrollment policy and Click Next. Choose No Template Legacy Key for compatibility reasons. Use PKCS#10.
-
Click Next and click Properties. Give a friendly name for the certificate and a description. Ensure that you hit Apply as soon as you are done with the tab.
-
Click on Subject tab and add all SAN values under “Alternative Name“. Under Subject Name, enter the Common Name (CN), Organizational Unit (OU), Organization (O), City (L), State (S), and 2 letter Country (C) code values. Click Apply.
-
Under the Extensions tab, expand Extended Key Usage (application policies) and select Server Authentication and Client Authentication. Click Apply.
-
Under the Private Key tab, set the Key size to 2048 (or 4096) under Key options. Tick Make Private Key exportable. Select Exchange as the Key type. Click Apply. Click OK.
-
Select a location to save the file. Choose the file format as Base 64. Click Finish.
CSR is generated with SAN values.
Tagged In
No Comments Yet.
How to generate correct CSR when IP address is in CN or SAN ?
When an internal/external IP Address is part of Common Name (CN) or Subject Alternative Name (SAN) care needs to be taken while generating the CSR.
If not done correctly then the latest browsers like Chrome and Edge give an error – “Your connection to this site is not secure.” Note that deprecated Microsoft Internet Explorer does not give any error in this case.
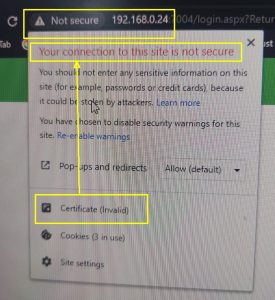
To avoid this problem please ensure that the IP address is mentioned in the SAN extension as DNS value and IP Address. For example, if CN=192.168.23.1 then the CSR should have 2 SAN values viz., DNS=192.168.23.1 and IP=192.168.23.1
If you wish to generate the CSR on Windows Server then read this FAQ. How to create the CSR with SAN in Windows IIS
If you wish to generate the CSR using OpenSSL then this link explains step-by-step how to generate the CSR using OpenSSL
Tagged In
No Comments Yet.
Is it compulsory to provide CSR to get Intranet SSL ?
Not necessary.
Just fill-up the form and we will generate the CSR (called Auto-CSR). And we will send the SSL Certificate along with the private key.
Tagged In
No Comments Yet.
While requesting Intranet SSL, should I generate CSR or just give certificate details ?
Good question.
It is always recommended to generate CSR on your web server and share with us. This is because the private key generated during the CSR generation remains on your server, within your premises.
On the other hand, if you give certificate details to us, we generate the CSR. It is called Auto-CSR. During this process, private key is generated on our machine. When we ship the Intranet SSL to you, we send the SSL certificate along with the private key. This method is slightly risky because the private key can be intercepted by someone when it is sent through email.
But generation of CSR for Intranet SSL poses some technical challenges. Reason is that modern browsers expect the CSR to have require SAN values correctly specified.
For example, if the Common Name is “abc.local” then the CN=abc.local and SAN value should be DNS=abc.local. But it is not easy to generate CSR with SAN values on Windows or Linux.
Another issue comes when the certificate is to be issued to an IP address. In this case SAN should have two values. They are DNS=[IP-address] and IP=[IP-Address].
If any of these SAN values are not specified while generating the CSR then browser gives 'Certificate not Trusted' error.
Of course, we have shared the steps to generate CSR with SAN values. Link is given below.
Tagged In
No Comments Yet.
How to create CSR with SAN on Windows Data Center Edition ?
To generate a CSR (Certificate Signing Request) with SAN (Subject Alternative Names) on Windows Server 2022 Datacenter Edition, the most straightforward and flexible method is using PowerShell with a custom INF file and the Certreq utility.
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
✅ Step 1: Create an INF File (Certificate Request File)
To create a CSR with CN with 2 DNS SANs and 2 IP SANs .Create a new text file named request.inf and paste the following content into it:
[Version]
Signature="$Windows NT$"
[NewRequest]
Subject = "CN=<CN>; O=<Org Name>; L=<City>; S=<state>; C=<2 Digit Country Code>"
KeySpec = 1
KeyLength = 2048
Exportable = TRUE
MachineKeySet = TRUE
SMIME = FALSE
PrivateKeyArchive = FALSE
UserProtected = FALSE
UseExistingKeySet = FALSE
ProviderName = "Microsoft RSA SChannel Cryptographic Provider"
ProviderType = 12
RequestType = PKCS10
KeyUsage = 0xa0
[Extensions]
2.5.29.17 = "{text}"
_continue_ = "dns=<CN>&"
_continue_ = "dns=<SAN-1>&"
_continue_ = "dns=<SAN-2>&"
_continue_ = "dns=<IP-1>&"
_continue_ = "dns=<IP-2>&"
_continue_ = "ip=<IP-1>&"
_continue_ = "ip=<IP-2>"
[RequestAttributes]
CertificateTemplate = WebServerCustomize these fields:
CN=Your primary domain name e.g., *.server.local Under [Extensions] → List all DNS SANs (dns=SAN) and all IP SANs with (dns=IP-address) and (ip=IP-address) separated by "&"
Add or remove SANs as needed
✅ Step 2: Generate the CSR Using certreq
Open PowerShell as Administrator and run:
certreq -new request.inf server.csrThis creates a CSR file named server.csr which you can submit to SecureNT.
✅ Step 3: Submit CSR to CA
If you are using a private CA (SecureNT), upload the CSR as part of your certificate request.
✅ Step 4: Install the SSL Certificate
After receiving the signed certificate (.cer or .crt), install it with:
certreq -accept server.cerTagged In
No Comments Yet.
Categories
Tags